Asteroids
Asteroids, the remnants of our early solar system, hold a wealth of scientific knowledge waiting to be unraveled. These celestial objects, often referred to as minor planets, are rocky bodies that orbit the Sun.
Ranging in size from mere pebbles to massive chunks of rock, asteroids can be found throughout our cosmic neighborhood. Understanding these fascinating objects is not only essential for exploring the origins of our solar system but also for inspiring future generations in the field of space science.
Small asteroids (a few meters in diameter): Can cause localized damage upon impact, equivalent to a small explosion. Damage may include structural destruction within a limited radius, potential injuries, and casualties.
Medium-sized asteroids (tens to hundreds of meters in diameter): Possess significantly more destructive potential. Impact can generate powerful shockwaves, leading to widespread devastation in the affected region. This can result in the leveling of buildings, extensive loss of life, and severe damage to the environment.
Large asteroids (several kilometers in diameter): Have catastrophic potential. Impact can release an unimaginable amount of energy, causing global-scale disasters. The consequences include massive seismic activity, the formation of tsunamis, and the release of debris and dust into the atmosphere. This can lead to long-term climate changes, devastating ecosystems, and even triggering mass extinctions.
Understanding the varying destructive power of asteroids highlights the critical importance of early detection systems, preparedness, and the development of effective mitigation strategies to protect our planet from these potential catastrophic events.
Asteroid Mining
Asteroid mining is a rapidly emerging field that aims to extract valuable resources from asteroids. These resources, which include precious metals, water, and rare elements, could fuel future space exploration and provide sustenance for manned missions beyond Earth. Several companies are actively involved in research and development efforts related to asteroid mining, seeking innovative ways to exploit these celestial bodies for the benefit of humanity.
Companies Engaged in Asteroid Mining
Here some companies leading the way in the field of asteroid mining:
| Company Name | Website |
|---|---|
| Deep Space Industries | www.deepspaceindustries.com |
| Asteroid Mining Corporation | www.asteroidminingcorp.com |
| Moon Express | www.moonexpress.com |
| TransAstra Corporation | www.transastracorp.com |
| Astroforge | www.astroforge.com |
| OffWorld | www.offworld.ai |
| Bradford Space | www.bradford-space.com |
| Lunar Outpost | www.lunaroutpost.com |
| iSpace | www.ispace-inc.com |
These companies are at the forefront of developing technologies, strategies, and business models for asteroid mining. Their efforts are focused on identifying and extracting valuable resources from asteroids, ultimately paving the way for a sustainable and prosperous future in space.
Note: This table represents a selection of prominent space companies involved in developing space tourism offerings. The industry is dynamic, and new players may emerge while existing companies continue to evolve their offerings. Please visit the respective website URLs for more information about each company’s space tourism initiatives.
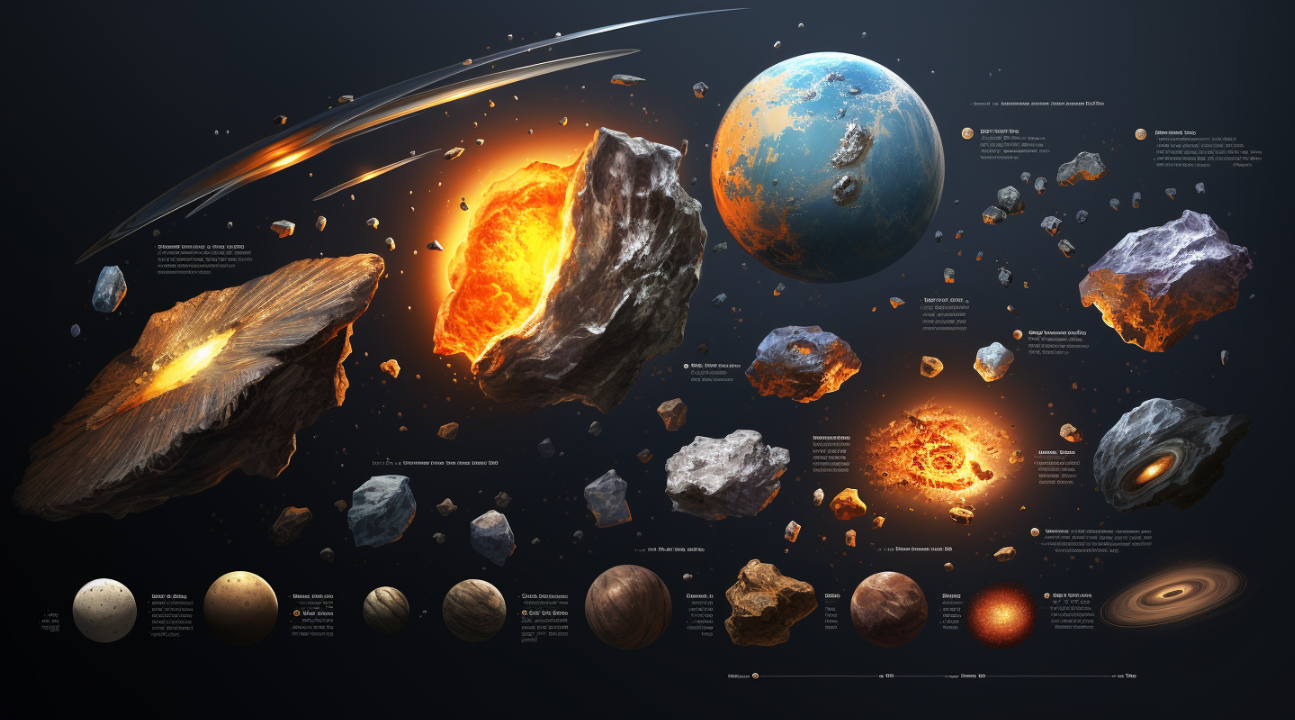
Asteroid Classification and Composition
Asteroids come in various shapes and sizes, and their composition can vary greatly. Most asteroids are composed of rock and metal, but some also contain valuable resources such as water and organic compounds. Scientists classify asteroids into different types based on their composition, providing valuable insights into their origins and formation processes. By studying the composition of asteroids, we can gain a better understanding of the building blocks that formed our planets and the potential resources they hold.
Asteroids as Time Capsules
Asteroids serve as time capsules, preserving the remnants of the early solar system. Within their rocky surfaces, scientists have discovered a treasure trove of information about the conditions that existed billions of years ago. By analyzing asteroid samples, researchers can unlock the secrets of the past, studying the isotopic composition and organic molecules that provide clues about the origins of life on Earth. These findings not only deepen our understanding of our own planet but also offer insights into the potential habitability of other celestial bodies.
Asteroid Exploration and Future Missions
Asteroid exploration has become a significant focus for space agencies worldwide. Missions such as NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and JAXA’s Hayabusa2 have successfully rendezvoused with asteroids, collected samples, and returned them to Earth for analysis. These missions have revolutionized our understanding of asteroids and paved the way for future endeavors. In the coming years, space agencies are planning ambitious missions to study and even mine asteroids. These missions hold the promise of unlocking valuable resources, furthering our scientific knowledge, and providing opportunities for space-based industries.
Ancient Observations of Asteroids
Since ancient times, humans have observed asteroids in the night sky, often unaware of their true nature. In ancient civilizations such as the Mesopotamians and Egyptians, celestial events, including asteroid sightings, were interpreted as omens or divine messages. Early humans marveled at the movements of these wandering stars, documenting their appearances and occasional unexpected changes in their trajectories.
It was not until the advancement of astronomy in the Renaissance period that our understanding of asteroids began to take shape. Visionaries like Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler, armed with telescopes and mathematical principles, made significant contributions to the field. Galileo, in particular, made observations of asteroids, then referred to as “stars,” and recorded their positions relative to the fixed stars.
Leonardo da Vinci, renowned for his scientific and artistic endeavors, also showed interest in celestial objects. His meticulous drawings of the Moon and celestial bodies, including comets and meteors, indicate an awareness of the existence and movement of asteroids in the night sky.
As the centuries progressed, astronomers such as Giuseppe Piazzi, William Herschel, and Charles Messier made remarkable discoveries, cataloging and mapping the positions of numerous asteroids. Their observations and diligent record-keeping laid the foundation for future research and the eventual understanding of asteroids as individual celestial bodies with distinct characteristics.


Today, modern telescopes, space missions, and advanced technologies have greatly expanded our knowledge of asteroids. With dedicated observatories and spacecraft, scientists continue to study these cosmic remnants, unraveling their mysteries and paving the way for future exploration and potential utilization.
Asteroids have captured the attention of humans since ancient times. From early civilizations interpreting their appearances as divine messages to the pioneering work of astronomers like Galileo Galilei, our understanding of these celestial bodies has evolved significantly.
Today, we continue to explore and study asteroids, unlocking their secrets and broadening our knowledge of the solar system’s origins.
Asteroids, once regarded as mysterious celestial wanderers, have now become a focal point of scientific exploration and potential commercial opportunities. From ancient civilizations interpreting their appearances as divine messages to the pioneering work of astronomers like Galileo Galilei, our understanding of these celestial bodies has evolved significantly. Today, we harness cutting-edge technologies and space missions to study and unlock the secrets of asteroids.
Asteroid mining has long captivated the imagination of scientists, entrepreneurs, and space enthusiasts, offering the tantalizing prospect of accessing vast resources and expanding humanity’s presence in space. The dream of extracting valuable minerals, water, and other elements from these celestial bodies ignites visions of fueling space exploration, enabling colonization, and revolutionizing industries. However, the reality of asteroid mining brings forth a myriad of challenges that must be overcome. Technological hurdles, legal complexities, environmental considerations, and ethical dilemmas present formidable obstacles on the path to turning this dream into a practical reality. In this article, we will explore the allure of asteroid mining, the vast potential it holds, and the daunting challenges that must be addressed for this extraordinary vision to be realized.
The Dream of Asteroid Mining:
Unlimited Resources: Asteroid mining holds the promise of accessing vast quantities of resources that are scarce or difficult to obtain on Earth. These resources include precious metals like platinum, rare elements critical for advanced technologies, and even water, which can be used for life support and fuel production in space.
Space Colonization: Successful asteroid mining operations could provide essential resources for space colonization efforts. By utilizing asteroid resources, we can reduce the cost and reliance on Earth for supplies, making long-duration space missions and establishing permanent settlements more feasible.
Economic Opportunities: The commercial potential of asteroid mining is enormous. Access to valuable resources in space could lead to the development of new industries, job creation, and economic growth. Companies involved in asteroid mining have the opportunity to pioneer a new frontier of space-based enterprises and reap the benefits of their ventures.
Advancements in Technology: The challenges of asteroid mining require technological innovations, driving advancements in robotics, mining techniques, and space infrastructure. These advancements have the potential to spin off into other industries and benefit humanity as a whole, leading to new technologies and engineering breakthroughs.
Scientific Discoveries: As we mine and study asteroids, we gain valuable insights into the formation of the solar system and the origins of life. The analysis of asteroid samples can deepen our understanding of the universe, provide clues about the conditions that led to the development of life on Earth, and potentially shed light on the existence of extraterrestrial life elsewhere.
Environmental Benefits: Asteroid mining offers the potential to reduce the environmental impact of resource extraction on Earth. By sourcing materials from space, we can alleviate the strain on our planet’s ecosystems and minimize destructive mining practices.
Space Exploration Expansion: Successful asteroid mining operations would provide essential resources for further space exploration. By utilizing resources found in space, we can extend our reach deeper into the cosmos, enabling more ambitious missions to other planets, moons, and even interstellar travel.
Energy and Infrastructure Independence: Accessing resources from asteroids could lead to greater energy independence in space. Water from asteroids can be broken down into hydrogen and oxygen, providing fuel for spacecraft and supporting human settlements. This self-sufficiency reduces the need for resupply missions from Earth and opens up possibilities for sustainable space exploration.
Inspiration and Human Achievement: The dream of asteroid mining captures the imagination and inspires future generations to pursue careers in STEM fields. By pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and technological capabilities, we showcase the power of human achievement and the boundless potential of exploring the unknown.
Preservation of Earth: The dream of asteroid mining aligns with the broader goal of preserving Earth and ensuring a sustainable future. By accessing resources from space, we can reduce our impact on our home planet and foster a greater appreciation for the fragility and uniqueness of Earth.
The dream of asteroid mining represents a paradigm shift in human capabilities and the exploration of space. With advancements in technology, continued research, and the dedication of scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs, this dream has the potential to become a reality, unlocking a new era of space exploration, resource utilization, and human achievement.
The Challenges and Dilemmas of Asteroid Mining:
Technological Hurdles: Asteroid mining poses significant technological challenges. Mining operations in space require advanced robotics, drilling techniques, and extraction methods that can withstand the harsh conditions and low gravity environments. Developing and implementing these technologies is crucial for the success of asteroid mining ventures.
Cost and Funding: The cost of asteroid mining missions is currently prohibitively high. The development of spacecraft, mining equipment, and the logistics involved in reaching and extracting resources from asteroids require substantial financial investment. Securing funding for such ventures is a major challenge and often necessitates collaborations between private entities and government agencies.
Legal and Regulatory Framework: The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding asteroid mining is complex and largely undeveloped. Questions regarding property rights, ownership of extracted resources, and the establishment of a framework for fair and sustainable practices need to be addressed. International cooperation and the development of clear legal frameworks are essential to ensure responsible and ethical asteroid mining operations.
Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of asteroid mining is an important consideration. Dust and debris generated during mining operations could pose risks to spacecraft, affect orbital dynamics, and potentially contribute to space debris. Balancing the extraction of resources with sustainable practices and mitigating any potential environmental harm is crucial for the long-term viability of asteroid mining.
Ethical Considerations: As we venture into asteroid mining, ethical questions arise regarding the preservation of celestial bodies and their scientific value. Some asteroids may hold unique scientific significance, and their pristine conditions should be preserved for future study. Establishing guidelines and practices that balance resource extraction with scientific preservation is a critical dilemma.
Space Traffic and Collision Risks: The increased presence of mining spacecraft and infrastructure around asteroids raises concerns about space traffic management and the potential for collisions. Clear protocols and coordination mechanisms are necessary to ensure the safety of spacecraft, protect existing satellites, and prevent the creation of hazardous debris fields.
Interplanetary Contamination: The extraction and utilization of asteroid resources carry the risk of interplanetary contamination. Care must be taken to prevent the introduction of potentially harmful or alien substances to Earth or other celestial bodies, safeguarding the integrity of ecosystems and future scientific exploration.
Public Perception and Acceptance: Public perception of asteroid mining can influence its progress and acceptance. Communicating the benefits, addressing concerns, and fostering public engagement are crucial for the long-term sustainability and support of asteroid mining ventures.
Economic Viability and Return on Investment: The economic viability of asteroid mining is a significant challenge. The market demand for extracted resources, along with the costs associated with mining and transportation, must be carefully evaluated to ensure a viable return on investment. Market fluctuations, resource prices, and competition from alternative sources also impact the economic feasibility of asteroid mining.
International Cooperation and Collaboration: Successful asteroid mining requires international cooperation and collaboration. Coordinating efforts, sharing resources and expertise, and establishing standards and protocols for responsible mining practices are essential for the sustainable development of asteroid mining on a global scale.
Navigating the challenges and dilemmas of asteroid mining requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving stakeholders from the scientific community, space agencies, private enterprises, and the public. By addressing these challenges head-on and developing sustainable solutions, we can unlock the potential of asteroid resources while ensuring responsible and ethical practices in the pursuit of space exploration and resource utilization.
In conclusion, space mining represents a transformative frontier that holds immense potential for humanity’s future. With its conservative approach, acknowledging the limitations and uncertainties of our current knowledge, space mining takes into account the dynamic nature of time and the evolution of technology. While the dream of accessing valuable resources from asteroids fuels our imagination, it is essential to recognize the intricate challenges and dilemmas that lie ahead. Through continued technological advancements, responsible practices, international collaboration, and a commitment to environmental preservation, we can navigate the complexities of space mining.
By embracing a time-relative perspective, we can adapt to the ever-changing landscape of space exploration, ensuring that our ventures into the cosmos are sustainable, ethical, and beneficial for generations to come. As we forge ahead, let us remain steadfast in our pursuit of knowledge, guided by the transformative power of technology, and driven by a shared vision of a prosperous future beyond our earthly boundaries.